Chapter 2: How Oil Heat Works
One of the advantages of oil heat is that you have options as to how you use it. Heating oil can be used in furnaces or oil systems. But how does heating oil work exactly?
How Does Oil Heat Work? Types of Oil Heating Systems
For both furnaces and boilers, you keep extra oil in outdoor storage tanks. However, there are several key differences to note in each of these types of oil heating systems:
- Furnaces. Atmospheric furnaces are older, less efficient models. Their name is derived from their venting system, where their gases go up through chimneys — and exhaust air has to be very hot in order for the venting process to work correctly. These furnaces lose about 30 percent of fuel energy by simply maintaining high enough temperatures to vent the gases.
 Modern minimum-efficiency furnaces are more effective. A fan pulls exhaust air through a heat exchanger. The fan creates a draft, and gases go up the chimney.When heating with oil, the most efficient furnaces are newer condensing models. Less heat escapes to the outside. Instead of immediately venting hot exhaust, these furnaces cool gases first. Therefore, water vapor condenses and exhaust travels outside through a plastic pipe in the sidewall.
Modern minimum-efficiency furnaces are more effective. A fan pulls exhaust air through a heat exchanger. The fan creates a draft, and gases go up the chimney.When heating with oil, the most efficient furnaces are newer condensing models. Less heat escapes to the outside. Instead of immediately venting hot exhaust, these furnaces cool gases first. Therefore, water vapor condenses and exhaust travels outside through a plastic pipe in the sidewall. - Boilers. Boilers are another type of oil heater. While furnaces heat air, hydronic boilers warm up water. The liquid travels through the house, providing heat through equipment such as radiators or baseboards. Cooled water then cycles back to the boiler for reheating.A less common oil heater is a steam boiler. After water boils, steam moves through the system, bringing heat to radiators. Steam then condenses, and the gases are vented through a sidewall or chimney.
The Oil Heat Mechanism
For both furnaces and boilers, the explanation for how oil heat works begins with a combustion chamber, where the oil ignites. Then a heat exchanger warms the gases or water flowing through the component.
In a furnace, a fan, or blower motor, pulls in household air from cold air return ducts and sends it through the heat exchanger. Heated air then goes through warm air ducts and circulates throughout the house. Cooled air cycles back to the furnace.
Boilers use pumps to propel heated water through pipes to radiators. Cooled water returns to the boiler for reuse.
Oil Heat Maintenance
Homeowners can take protective measures to keep their oil heaters in good shape, like noting the color of the chimney smoke. For instance, black smoke indicates wasted fuel and reduced system efficiency.
Homeowners can take proactive steps as well when they are heating with oil. Cleaning the thermostat before heating season starts helps to regulate temperatures. Both the blower and the stack control component, which monitor the burner, benefit from cleaning halfway through the season. Regular upkeep removes particles and deposits that impede function.
Though both types of oil heaters should be examined and refreshed annually, sometimes a professional must step in. Even with regular yearly checkups, a homeowner could need a technician to handle a specific problem, such as cleaning a burner, unblocking the fuel line or fixing a faulty ignition spark.
 Download the full guide!
Download the full guide!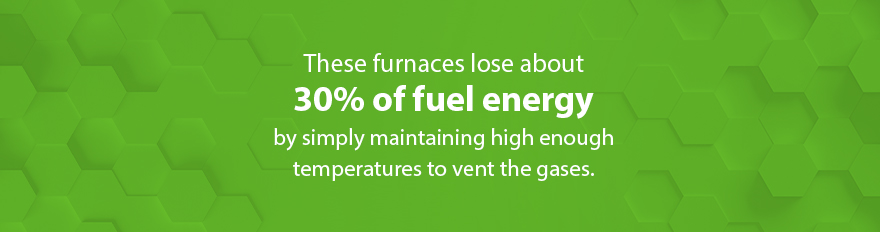 Modern minimum-efficiency furnaces are more effective. A fan pulls exhaust air through a heat exchanger. The fan creates a draft, and gases go up the chimney.When heating with oil, the most efficient furnaces are newer condensing models. Less heat escapes to the outside. Instead of immediately venting hot exhaust, these furnaces cool gases first. Therefore, water vapor condenses and exhaust travels outside through a plastic pipe in the sidewall.
Modern minimum-efficiency furnaces are more effective. A fan pulls exhaust air through a heat exchanger. The fan creates a draft, and gases go up the chimney.When heating with oil, the most efficient furnaces are newer condensing models. Less heat escapes to the outside. Instead of immediately venting hot exhaust, these furnaces cool gases first. Therefore, water vapor condenses and exhaust travels outside through a plastic pipe in the sidewall.